Contour Canary Deployments
This guide shows you how to use Contour ingress controller and Flagger to automate canary releases and A/B testing.
Prerequisites
Flagger requires a Kubernetes cluster v1.16 or newer and Contour v1.0 or newer.
Install Contour on a cluster with LoadBalancer support:
The above command will deploy Contour and an Envoy daemonset in the projectcontour namespace.
Install Flagger using Kustomize (kubectl 1.14) in the projectcontour namespace:
The above command will deploy Flagger and Prometheus configured to scrape the Contour's Envoy instances.
Or you can install Flagger using Helm v3:
You can also enable Slack, Discord, Rocket or MS Teams notifications, see the alerting docs.
Bootstrap
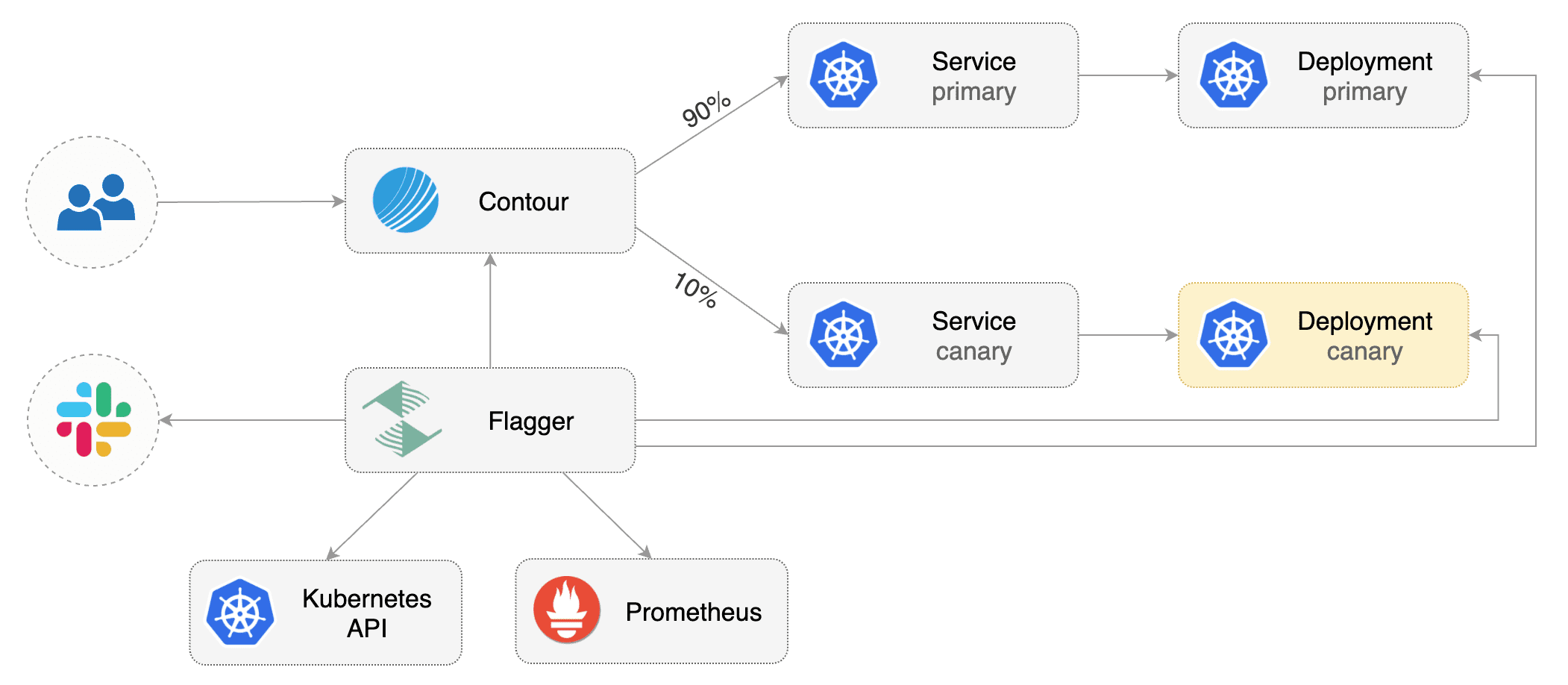
Flagger takes a Kubernetes deployment and optionally a horizontal pod autoscaler (HPA), then creates a series of objects (Kubernetes deployments, ClusterIP services and Contour HTTPProxy). These objects expose the application in the cluster and drive the canary analysis and promotion.
Create a test namespace:
Install the load testing service to generate traffic during the canary analysis:
Create a deployment and a horizontal pod autoscaler:
Create a canary custom resource (replace app.example.com with your own domain):
Save the above resource as podinfo-canary.yaml and then apply it:
The canary analysis will run for five minutes while validating the HTTP metrics and rollout hooks every half a minute.
After a couple of seconds Flagger will create the canary objects:
After the bootstrap, the podinfo deployment will be scaled to zero and the traffic to podinfo.test will be routed to the primary pods. During the canary analysis, the podinfo-canary.test address can be used to target directly the canary pods.
Expose the app outside the cluster
Find the external address of Contour's Envoy load balancer:
Configure your DNS server with a CNAME record (AWS) or A record (GKE/AKS/DOKS) and point a domain e.g. app.example.com to the LB address.
Create a HTTPProxy definition and include the podinfo proxy generated by Flagger (replace app.example.com with your own domain):
Save the above resource as podinfo-ingress.yaml and then apply it:
Verify that Contour processed the proxy definition with:
Now you can access podinfo UI using your domain address.
Note that you should be using HTTPS when exposing production workloads on internet. You can obtain free TLS certs from Let's Encrypt, read this guide on how to configure cert-manager to secure Contour with TLS certificates.
Automated canary promotion
Flagger implements a control loop that gradually shifts traffic to the canary while measuring key performance indicators like HTTP requests success rate, requests average duration and pod health. Based on analysis of the KPIs a canary is promoted or aborted.
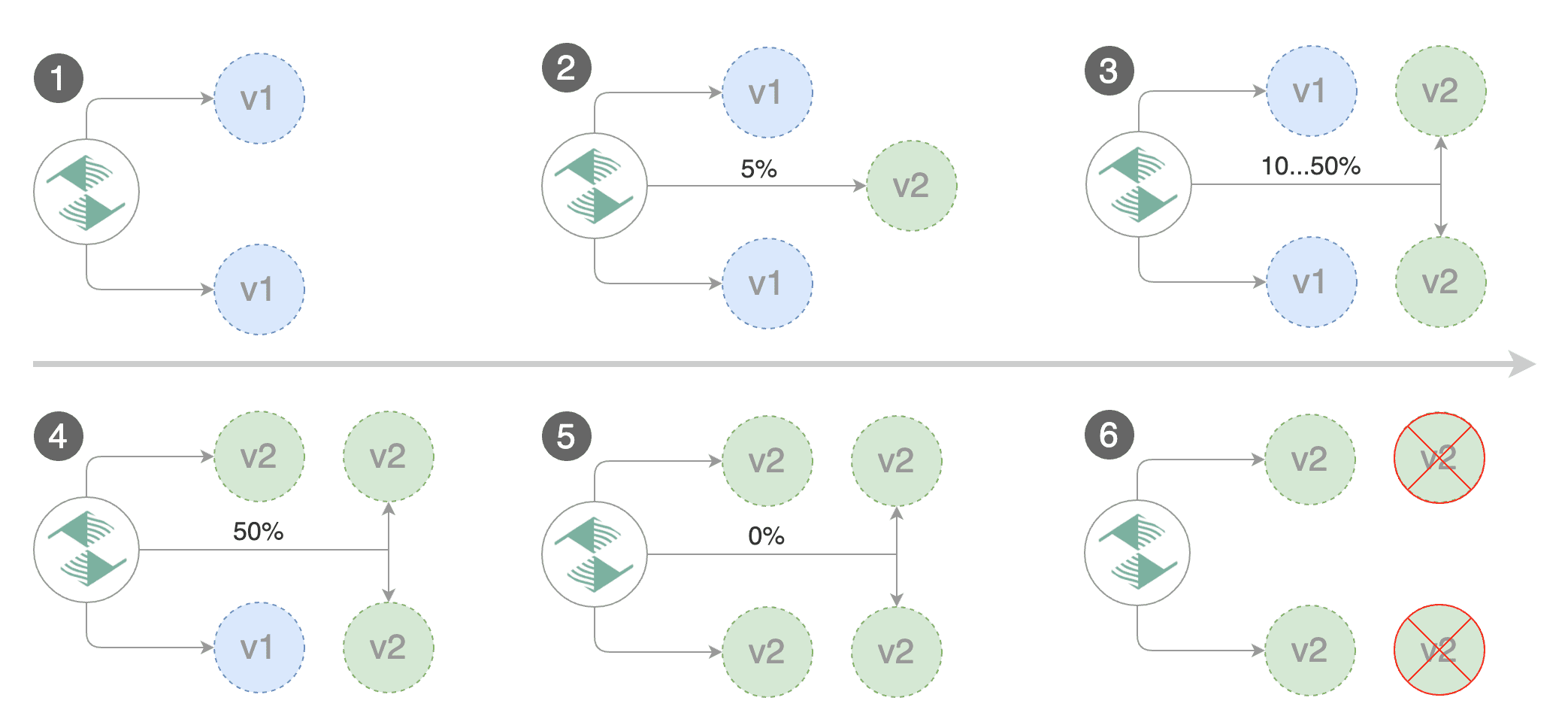
A canary deployment is triggered by changes in any of the following objects:
Deployment PodSpec (container image, command, ports, env, resources, etc)
ConfigMaps and Secrets mounted as volumes or mapped to environment variables
Trigger a canary deployment by updating the container image:
Flagger detects that the deployment revision changed and starts a new rollout:
When the canary analysis starts, Flagger will call the pre-rollout webhooks before routing traffic to the canary.
Note that if you apply new changes to the deployment during the canary analysis, Flagger will restart the analysis.
You can monitor all canaries with:
If you’ve enabled the Slack notifications, you should receive the following messages:

Automated rollback
During the canary analysis you can generate HTTP 500 errors or high latency to test if Flagger pauses the rollout.
Trigger a canary deployment:
Exec into the load tester pod with:
Generate HTTP 500 errors:
Generate latency:
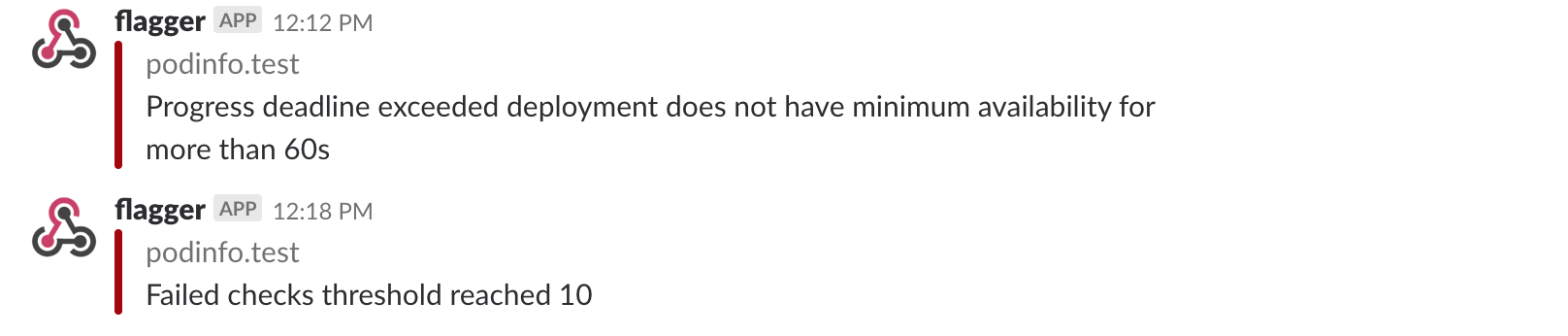
When the number of failed checks reaches the canary analysis threshold, the traffic is routed back to the primary, the canary is scaled to zero and the rollout is marked as failed.
If you’ve enabled the Slack notifications, you’ll receive a message if the progress deadline is exceeded, or if the analysis reached the maximum number of failed checks:
A/B Testing
Besides weighted routing, Flagger can be configured to route traffic to the canary based on HTTP match conditions. In an A/B testing scenario, you'll be using HTTP headers or cookies to target a certain segment of your users. This is particularly useful for frontend applications that require session affinity.
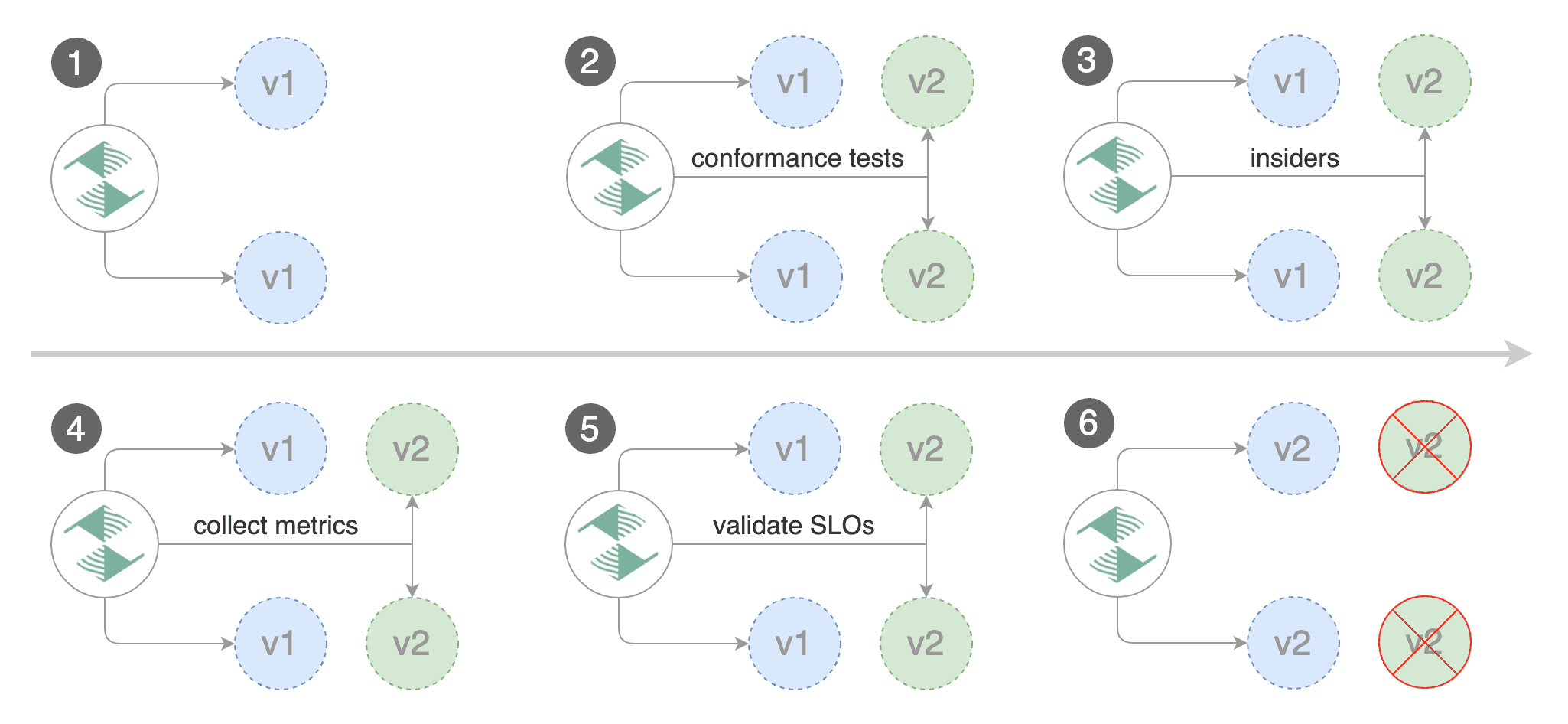
Edit the canary analysis, remove the max/step weight and add the match conditions and iterations:
The above configuration will run an analysis for ten minutes targeting users that have a X-Canary: insider header.
You can also use a HTTP cookie. To target all users with a cookie set to insider, the match condition should be:
Trigger a canary deployment by updating the container image:
Flagger detects that the deployment revision changed and starts the A/B test:
The web browser user agent header allows user segmentation based on device or OS.
For example, if you want to route all mobile users to the canary instance:
Or if you want to target only Android users:
Or a specific browser version:
For an in-depth look at the analysis process read the usage docs.
Last updated
Was this helpful?