Knative Canary Deployments
This guide shows you how to use Knative and Flagger to automate canary deployments.
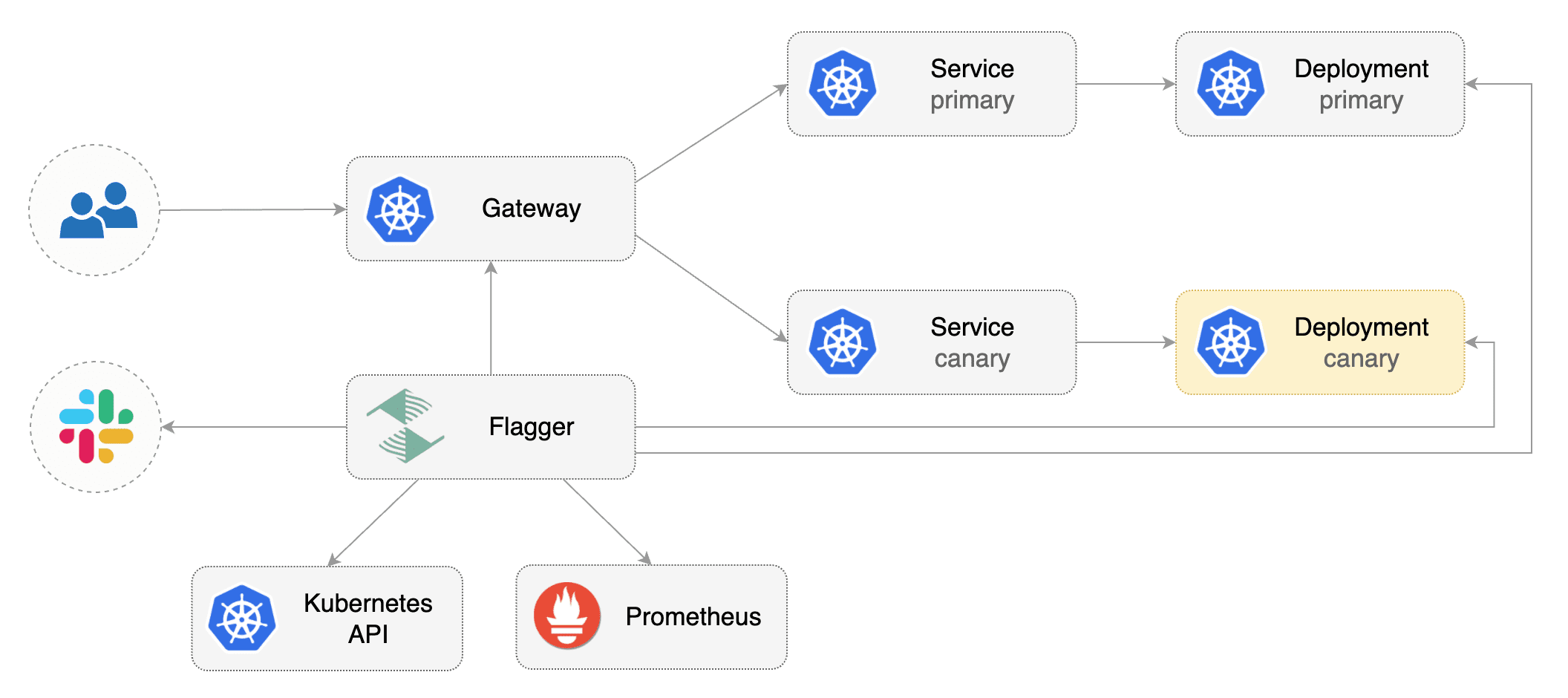
Prerequisites
Flagger requires a Kubernetes cluster v1.19 or newer and a Knative Serving installation that supports the resources with serving.knative.dev/v1 as their API version.
Install Knative v1.17.0:
Install Flagger in the flagger-system namespace:
Create a namespace for your Kntive Service:
Create a Knative Service that deploys podinfo:
Deploy the load testing service to generate traffic during the canary analysis:
Create a Canary custom resource:
Note: Please note that for a Canary resource with
.spec.providerset toknative, the resource is only valid if the.spec.targetRef.kindisServiceand.spec.targetRef.apiVersionisserving.knative.dev/v1.
Save the above resource as podinfo-canary.yaml and then apply it:
When the canary analysis starts, Flagger will call the pre-rollout webhooks before routing traffic to the canary. The canary analysis will run for five minutes while validating the HTTP metrics and rollout hooks every minute.
After a couple of seconds Flagger will make the following changes the Knative Service podinfo:
Add an annotation to the object with the name
flagger.app/primary-revision.Modify the
.spec.trafficsection of the object such that it can manipulate the traffic spread between the primary and canary Knative Revision.
Automated canary promotion
Trigger a canary deployment by updating the container image:
Flagger detects that the deployment revision changed and starts a new rollout:
A canary deployment is triggered everytime a new Knative Revision is created.
Note that if you apply new changes to the Knative Service during the canary analysis, Flagger will restart the analysis.
You can monitor how Flagger progressively changes the Knative Service object to spread traffic between Knative Revisions:
You can monitor all canaries with:
Automated rollback
During the canary analysis you can generate HTTP 500 errors and high latency to test if Flagger pauses the rollout.
Trigger another canary deployment:
Exec into the load tester pod with:
Generate HTTP 500 errors:
Generate latency:
When the number of failed checks reaches the canary analysis threshold, the traffic is routed back to the primary Knative Revision and the rollout is marked as failed.
Last updated
Was this helpful?