Skipper Canary Deployments
This guide shows you how to use the Skipper ingress controller and Flagger to automate canary deployments.
Prerequisites
Flagger requires a Kubernetes cluster v1.19 or newer and Skipper ingress v0.13 or newer.
Install Skipper ingress-controller using upstream definition.
Certain arguments are relevant:
Install Flagger using kustomize:
Bootstrap
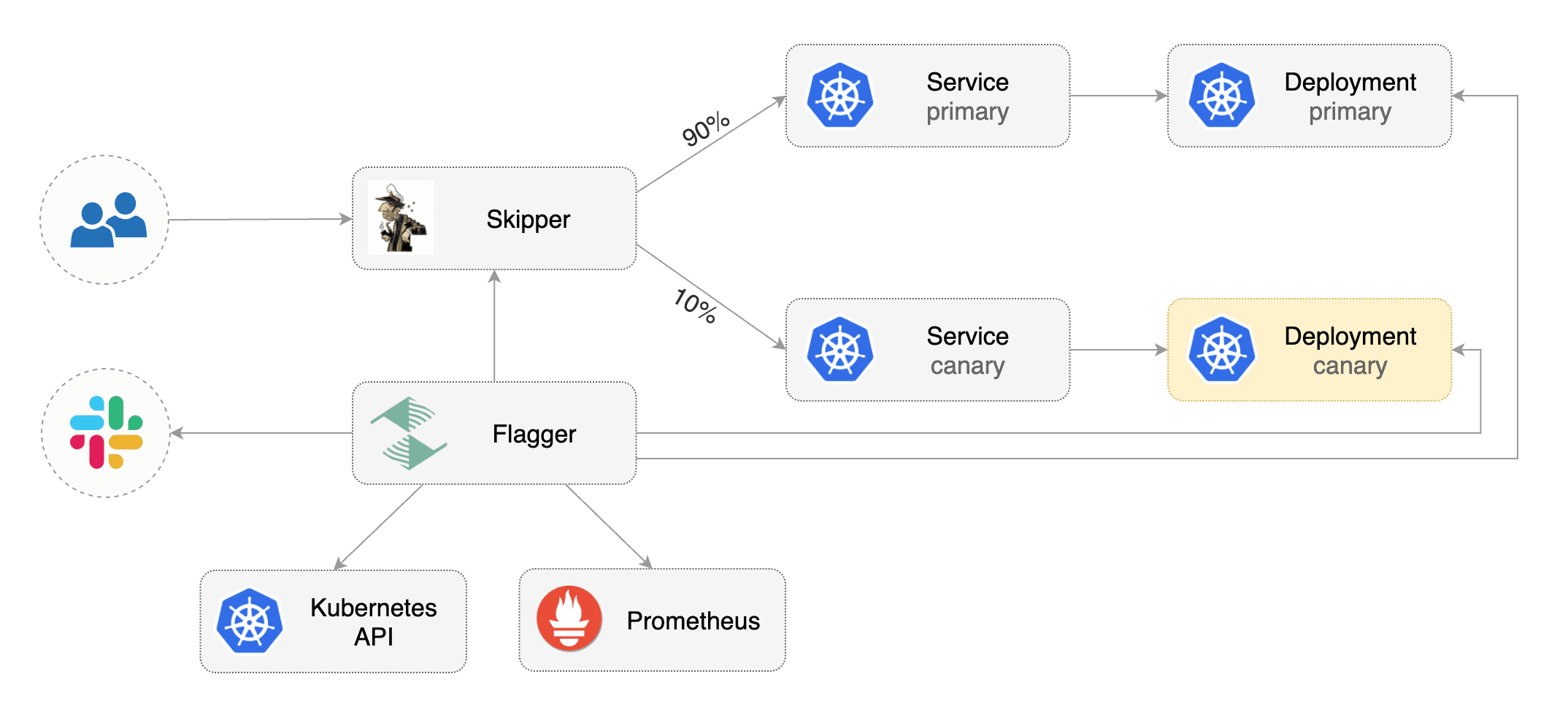
Flagger takes a Kubernetes deployment and optionally a horizontal pod autoscaler (HPA), then creates a series of objects (Kubernetes deployments, ClusterIP services and canary ingress). These objects expose the application outside the cluster and drive the canary analysis and promotion.
Create a test namespace:
Create a deployment and a horizontal pod autoscaler:
Deploy the load testing service to generate traffic during the canary analysis:
Create an ingress definition (replace app.example.com with your own domain):
Save the above resource as podinfo-ingress.yaml and then apply it:
Create a canary custom resource (replace app.example.com with your own domain):
Save the above resource as podinfo-canary.yaml and then apply it:
After a couple of seconds Flagger will create the canary objects:
Automated canary promotion
Flagger implements a control loop that gradually shifts traffic to the canary while measuring key performance indicators like HTTP requests success rate, requests average duration and pod health. Based on analysis of the KPIs a canary is promoted or aborted, and the analysis result is published to Slack or MS Teams.
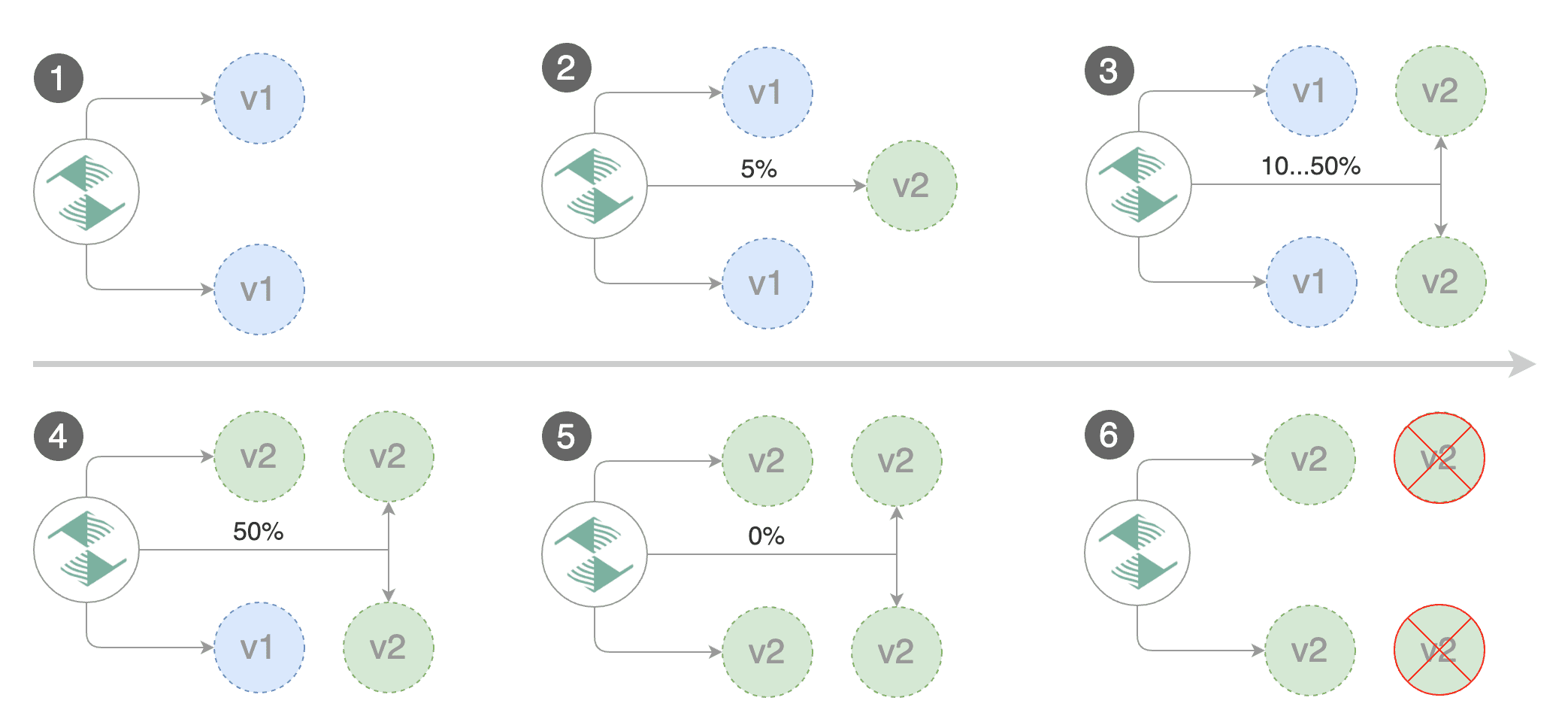
Trigger a canary deployment by updating the container image:
Flagger detects that the deployment revision changed and starts a new rollout:
Note that if you apply new changes to the deployment during the canary analysis, Flagger will restart the analysis.
You can monitor all canaries with:
Automated rollback
During the canary analysis you can generate HTTP 500 errors to test if Flagger pauses and rolls back the faulted version.
Trigger another canary deployment:
Exec into the load tester pod with:
Generate HTTP 500 errors:
Generate latency:
When the number of failed checks reaches the canary analysis threshold, the traffic is routed back to the primary, the canary is scaled to zero and the rollout is marked as failed.
Custom metrics
The canary analysis can be extended with Prometheus queries.
Create a metric template and apply it on the cluster:
Edit the canary analysis and add the latency check:
The threshold is set to 500ms so if the average request duration in the last minute goes over half a second then the analysis will fail and the canary will not be promoted.
Trigger a canary deployment by updating the container image:
Generate high response latency:
Watch Flagger logs:
If you have alerting configured, Flagger will send a notification with the reason why the canary failed.
Last updated
Was this helpful?